Tweeter
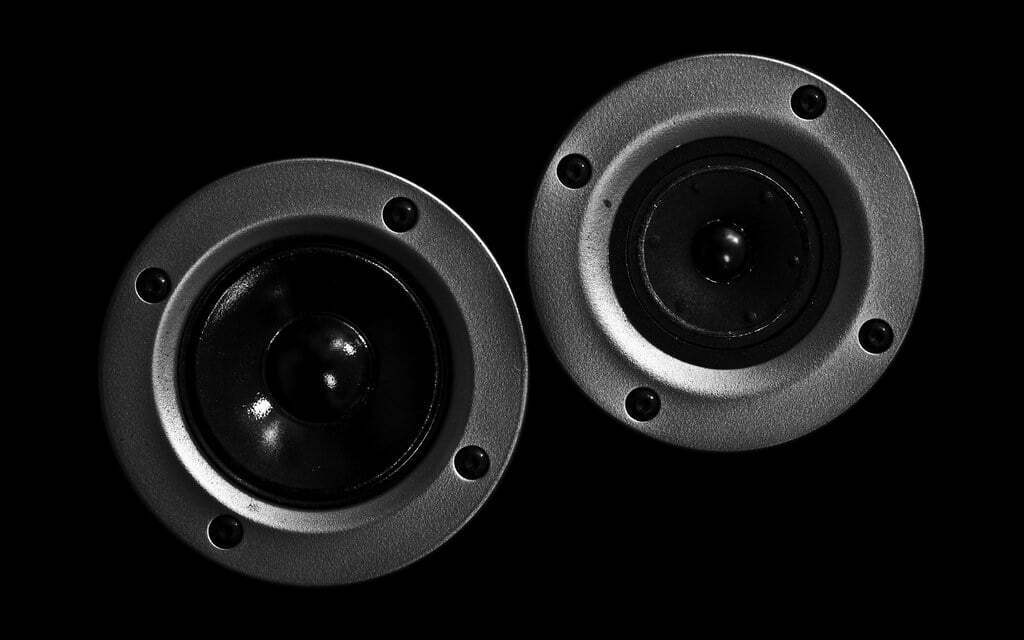
A tweeter is a type of speaker that is specifically designed to produce high-frequency sounds, such as the sibilant sounds in speech (s, sh, ch, etc.) and high-pitched musical instruments such as cymbals, violin and flute. Tweeters are often smaller in size compared to other types of speakers and are used in conjunction with other speakers, such as woofers, to produce a full and balanced sound.
Tweeters are typically smaller in size because they are designed to produce high-frequency sounds, which have shorter wavelengths and therefore require less air movement to produce the same volume as low-frequency sounds. This means that a smaller diaphragm can be used in a tweeter, making it more compact in size.
Another factor that contributes to the smaller size of tweeters is that they are often designed to work at higher frequencies, which are more directional and therefore require less dispersion. This allows for a smaller diaphragm to be used without sacrificing performance.
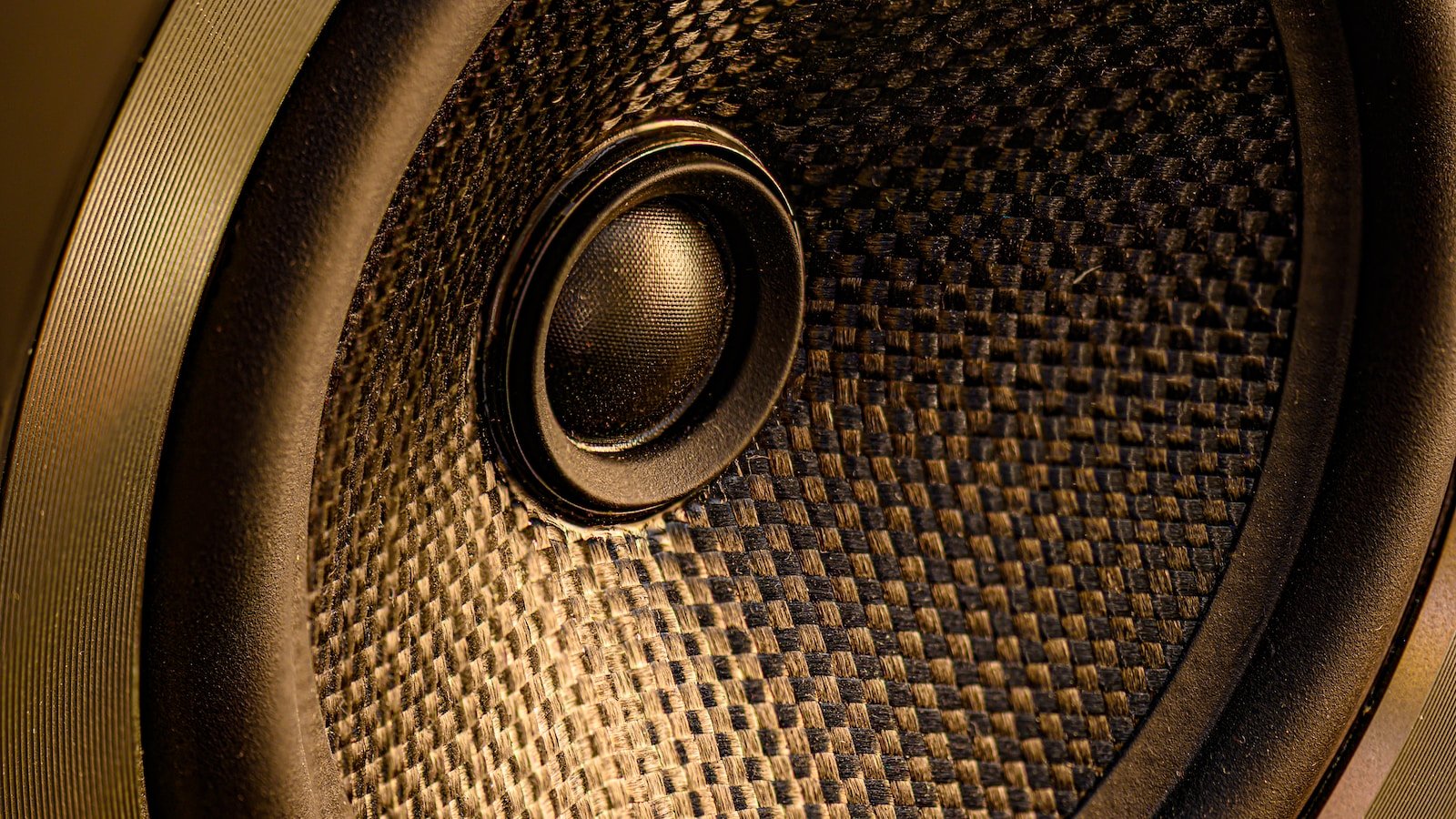

A subwoofer, on the other hand, is a type of speaker that is designed to produce low-frequency sounds, such as bass and drums. Subwoofers are typically larger in size than other types of speakers and are used to enhance the low-frequency response of a sound system. They are often used in home theater systems, music systems, and car audio systems to produce deep and powerful bass.
Subwoofers are larger in size because they require a larger diaphragm (or cone) in order to produce low-frequency sounds effectively. Low-frequency sounds have longer wavelengths and therefore require more air movement to produce the same volume as higher frequency sounds. This means that the diaphragm of a subwoofer needs to be larger in order to move enough air to produce these sounds.
Additionally, the larger size of a subwoofer allows for a larger voice coil and magnet, which are essential components for generating the electrical signals that drive the diaphragm. The larger size also allows for more power handling, which is important for producing deep and powerful bass.Why separate speakers?
Tweeters and subwoofers are separated in a sound system because each type of speaker is designed to handle a different frequency range. Tweeters are optimized for high-frequency sounds, while subwoofers are optimized for low-frequency sounds.
If high-frequency and low-frequency sounds were played through the same speaker, the diaphragm of the speaker would have to move a large amount of air to accommodate both the high-frequency and low-frequency sounds. This would be very difficult for a single speaker to handle, and would result in a distorted and unbalanced sound.
By separating the high-frequency and low-frequency sounds into separate speakers, each speaker is optimized to handle a specific frequency range, which results in a clearer and more balanced sound. Tweeters can reproduce high-frequency sounds with greater accuracy and clarity, while subwoofers can produce deep and powerful bass.
Additionally, separating the high-frequency and low-frequency sounds into separate speakers allows for more precise control over the soundstage, which can result in a more immersive and enjoyable listening experience.2-way and 3-way speakers
2-way and 3-way speakers are terms used to describe the number of individual speaker drivers that are included in a single speaker unit.
2-way speakers include two individual drivers: one for handling the high-frequency sounds (tweeter) and one for handling the low-frequency sounds (woofer). These speakers are often compact and cost-effective, and they provide a balanced and clear sound across the entire frequency spectrum.
3-way speakers, on the other hand, include three individual drivers: one for the high-frequency sounds (tweeter), one for the mid-frequency sounds (midrange), and one for the low-frequency sounds (woofer). These speakers provide a more detailed and nuanced sound than 2-way speakers, as the dedicated midrange driver allows for more accurate reproduction of the important mid-frequency sounds. 3-way speakers are often used in high-end home theater systems and music systems.
To divide an audio signal into separate frequency bands, an electronic component called Crossover is used. The crossover will then send each frequency band to the appropriate speaker drivers for reproduction.
The role of the crossover is to ensure that each speaker driver in a multi-way speaker system is only handling the frequencies for which it is optimized. For example, in a 3-way speaker system, the crossover would divide the audio signal into three separate frequency bands: high-frequencies for the tweeter, mid-frequencies for the midrange driver, and low-frequencies for the woofer.
This division of the audio signal allows each speaker driver to focus on reproducing a specific range of frequencies, which results in a more accurate and balanced sound. Without a crossover, each speaker driver would be trying to handle the entire frequency spectrum, which would likely result in distortion and an unbalanced sound.
In conclusion, knowing about tweeters and subwoofers can help you make informed decisions about other components in your sound system, such as crossovers, amplifiers, and soundproofing materials. Understanding the basic principles of speaker design and operation can help you choose and fine-tune your sound system for optimal performance, and can also enhance your overall listening experience.